Lunar Helium-3 Mining, LLC (LH3M) secured its fifth US patent last month, covering the company’s end-to-end architecture for He-3 detection, extraction, and refinement on the Moon.
LH3M is very much in the development phase, but with patents in hand, the company has begun talks with two rover companies—one in the US and one in Europe—to potentially ship LH3M tech to the Moon before the end of the decade, CEO Chris Salvino told Payload.
Look sharp: Lunar regolith is famously abrasive; during the Apollo missions, it made astronauts sneeze and ate away their space boots. LH3M believes their patents give them the winning formula. Salvino argues that lunar mining tech, which relies less on moving parts, could be less prone to breaking down.
LH3M is also confident that it won’t need to dig too deep, as most lunar He-3 lies in the first three-to-four cm of regolith—without anything churning the surface of the moon, solar wind derived He-3 should be sitting just on top.
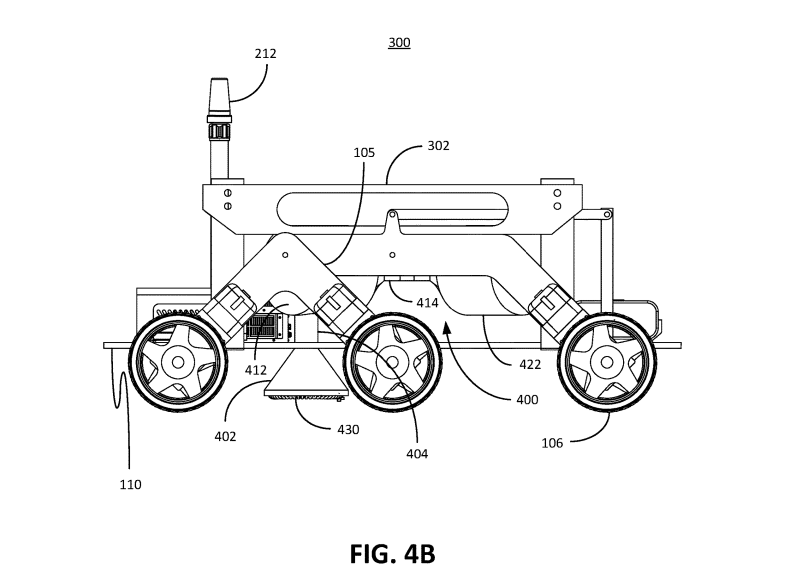
The company plans to fit up to three patented He-3 detection methods to a partner rover—a mass spectrometer, a neutron detection system, and an advanced imaging system. LH3M would then heat the surface regolith under the rover, suck up the resulting gasses into a containment system, extract the He-3, and then use a partner to return the samples back to Earth.
Moving parts: LH3M’s main competition, Interlune, has secured orders for lunar He-3, and unveiled the prototype excavator it aims to send to the lunar surface in 2027.
Getting there first is only a part of the battle. While demand for He-3—which is used for medical imaging, quantum computing, and fusion energy—outstrips the current supply, getting it back from the Moon is no simple task. Even at $20M per kg, lunar mining companies will need to create a mass-efficient extraction-and-return path to turn a profit.
“We founded the company based on using lunar techniques of extraction, not earth-based techniques,” Salvino said. “You just can’t go there like some bull in a china shop, and expect to use Earth-based mining techniques.” LH3M’s technique bets on the fact that regolith and moving parts won’t mix well.
Don’t go alone: LH3M’s vision of a lunar mining economy is complicated. Salvino believes He-3 is the only money-making resource on the Moon, but LH3M’s business model requires many other companies to build supporting infrastructure to make extraction possible and economically viable.
“The infrastructure has to be built around us. We’re not going to build the rover chassis. We’re not going to build the rocket. We’re not going to build the EVA suits for the astronauts to repair this stuff,” Salvino said. “Ultimately…it’s probably Starship.”
If LH3M can break into this ecosystem, however, Salvino expects the demand—from quantum computing and fusion energy alone—to support 100 or more He-3 mining rovers working full-time.