Citi released a report earlier this month titled “Space: The Dawn of a New Age.” The bank’s GPS group sizes up the commercial space market and forecasts that the sector will generate $1 trillion in annual sales by 2040.
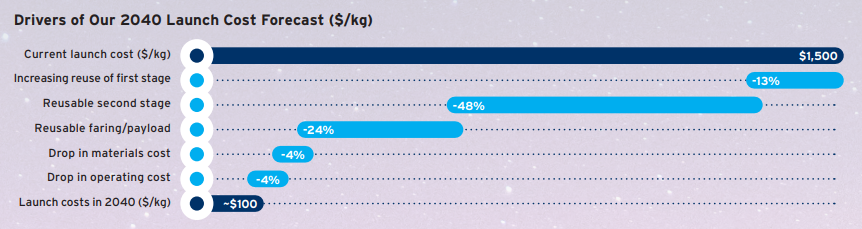
Big, if true…the shiny trillion-dollar number would represent a 5% compound annual growth rate from $370B of revenue in 2020. Citi analysts write that today’s launch costs—$1,500 per kilogram—could shrink to ~$100/kg by 2040. Or…$300/kg in a bear case scenario and $33/kg in a bull case one. The biggest driver in reducing launch costs is reusable second rocket stages:
While launch gets most of the headlines—and is undoubtedly eliminating barriers of entry in space—the satellite sector still dominates the market, in terms of value. Satellites make up 70+% of today’s space market. Citi analysts envision satellites growing to $697B by 2040, or roughly 69% of the total space industry.
- Over the next decade and a half, internet broadband and space-as-a-service applications should siphon away market share from traditional use cases like video broadcasting.
- Future segments, such as space-based solar power, orbital logistics, and Moon/asteroid mining, could kick in ~$100B in annual sales by 2040.
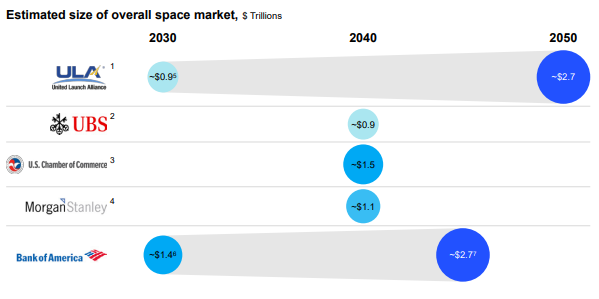
But…Forward-looking space economy research is highly speculative, hinging on extrapolation and plenty of if-then statements. In a report published last week, management consultant McKinsey highlights the wide divergence in forecasts about long-term growth of the space economy:
Snapshots in time: To level-set, the US space economy in 2019 accounted for $125B+ in real GDP output (or .6% of total US GDP) and 355,000+ private sector jobs, per BEA data. Usefully, McKinsey aggregated some other key stats in its report:
- The global space economy hit a new high of ~$447 billion in 2020.
- More than $12B in private funding is flowing into the sector annually.
- Around 70 countries have their own space agency.
- Roughly 4,850 satellites are operational on-orbit and ~1,740 small satellites are launched each year.





