Helicity Space, an in-space nuclear fusion propulsion startup, nabbed a $5M seed round to begin developing its novel engine.
The funding will allow the Pasadena, CA-based company to advance R&D of its recent breakthrough discovery of extremely stable plasma jets used for fusion reaction. Investors include Airbus Ventures, TRE Advisors, Voyager Space Holdings, E2MC Space, Urania Ventures, and Gaingels.
Fusion 101: Nuclear fusion (the opposite reaction to the more common fission) is the process that powers the sun. However, harnessing the energy source on Earth—let alone in space—has proven difficult, with only one net energy fusion reaction ever achieved.
Mini-sun engines: If and when it can be mastered, fusion could offer a near-inexhaustible energy source, potentially revolutionizing space propulsion by allowing spacecraft to travel farther, faster.
“In the space sector, fusion propulsion has been the holy grail since the 60s,” Helicity cofounder Stephane Lintner told Payload. “Fusion is the only reaction that gets you a level of energy that allows you to break away from the limits that we have right now with chemical.”
- Conventional chemical propulsion generates very high power but expends fuel quickly.
- Electric propulsion is fuel-efficient but is limited by power and thrust.
Mars, Jupiter, interstellar: The company says that when its Helicity Drive engines are operational (at least 10+ years out), it could propel a spacecraft to Mars in two months, Jupiter in one year, and interstellar space in just ten years. For comparison, it took NASA’s Perseverance rover about seven months to reach the Red Planet.
The company and its investors are well aware of the magnitude of the work ahead. Helicity will have to master the fusion reaction before it can look ahead to developing operational engines. The company’s product roadmap:
- 2026: Demo its plasma jets reconnecting—before fusion net gain.
- 2032: Test flight with fusion augmenting solar electric propulsion.
- 2040s: Self-sustaining engines.
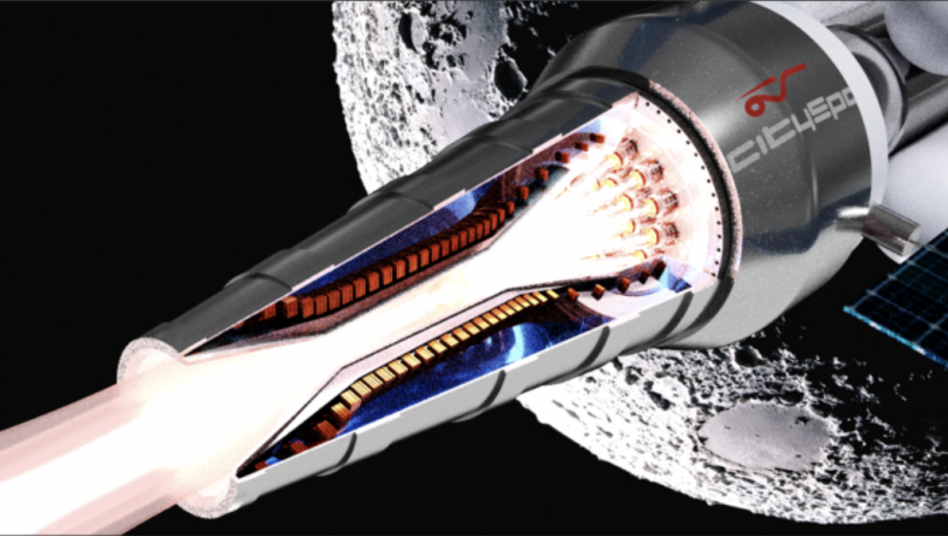
Geek out: Helicity’s fusion engines will employ a pulsed magneto-inertial confinement technique. How it works:
- Multiple plasma jets are shot along a track in the engine.
- The jets merge and compress, reaching fusion conditions at 100M degrees Fahrenheit.
- The fusion reaction fuses deuterium (hydrogen) atoms, resulting in energy for direct thrust.