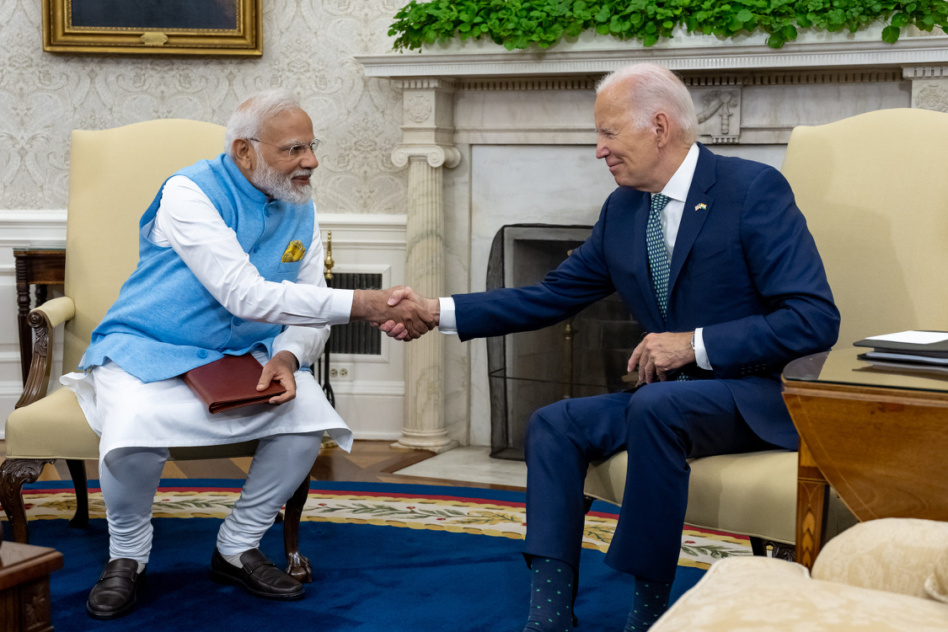
From human spaceflight to responsible use of space, the US and India announced a number of space-related agreements during Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s state visit to the White House on Thursday.
“We are creating a strong and futuristic partnership,” Modi said at a joint press conference, highlighting the new agreements in space.
Ready to launch: NASA and ISRO will work together on a pair of human spaceflight initiatives, according to a White House fact sheet:
- NASA will help train ISRO astronauts in Texas, with a longer-term goal of launching a joint mission to the ISS in 2024.
- The two space agencies are also working on a strategic framework for human spaceflight cooperation, which is set to be completed by the end of the year.
Hardware: The leaders announced a commitment to increased commercial collaboration and technology transfer, in addition to partnership on three specific missions:
- India is spending $318M on a Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory in the country that will study the origins of the universe in partnership with similar facilities in the US, Europe, and Japan.
- A joint synthetic aperture radar spacecraft that will launch in 2024 to study climate change has been delivered to India.
- There will be increased data sharing between the US Landsat program and ISRO’s Resourcesat program.
Diplomacy in orbit: India also became the 27th signatory to the Artemis Accords—and the second this week, after Ecuador joined in a ceremony at its embassy in DC on Wednesday.
“By making the decision to join the Artemis Accords, we have taken a big leap forward in our space cooperation,” Modi said. “In short, for the India and America partnership, even the sky is not the limit.”
A quick note: While space agreements have been part of multiple recent international visits to DC, they are typically buried in the joint statement and not mentioned in any public engagements. Modi’s mention of space during the press conference (and listing space priorities as the third of 58 bullets in the joint statement), shows that the leaders are really highlighting the significance.