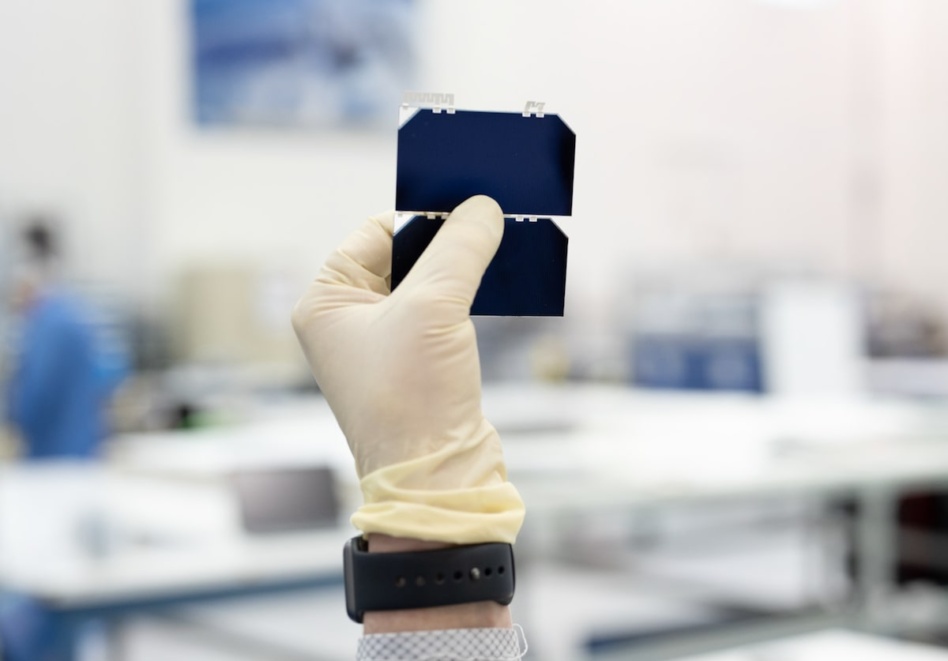
Rocket Lab and the Department of Commerce have reached a preliminary agreement to provide the company with $23.9M from the CHIPS Act to expand production of its advanced solar cells.
The plan, which also includes $25M in incentives from the state of New Mexico and capital investment from Rocket Lab, would create 100 manufacturing jobs at the company’s facility in Albuquerque, which the US-New Zealand firm acquired when it bought SolAereo in 2022.
After a due diligence process, Rocket Lab and the government will need to agree on a final term sheet later this year. If all goes as expected, construction could start early in 2025, Rocket Lab VP for Space Systems Brad Clevenger told Payload.
Why does Uncle Joe want in? Rocket Lab is one of three major players in the Western market that builds space-grade solar panels, and the investment will grow production 50% in the next three years. These cells are already on board the JWST, the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter, and OneWeb’s internet satellites, for a few examples.
The CHIPS and Science Act, which became law in 2022, is designed to increase manufacturing of advanced technology in the US, particularly to protect supply chains for components that are seen as vital to national security—an area where China often has an edge over the US. The SDA is particularly concerned about parts for spacecraft used by military and intelligence agencies.
What kind of chips are these? Most semiconductor uses, including microprocessors and photovoltaics, rely on silicon because it is cheap and widely available, but compound semiconductors made of multiple elements are more flexible for speciality applications such as in space.
The semiconductors made by Rocket Lab can withstand high doses of radiation and UV light, and generate more electricity in space than silicon equivalents.
“Every investment that they make here is dual use,” Clevenger says. “It helps the US space economy, and our ability to service commercial customers, and make sure that national security space has a place to have their needs met.”
Clevenger says that one of the reasons Rocket Lab won its $515M prime SDA contract was because of access to critical components like these solar cells.