Image: NASA/JPL-Caltech
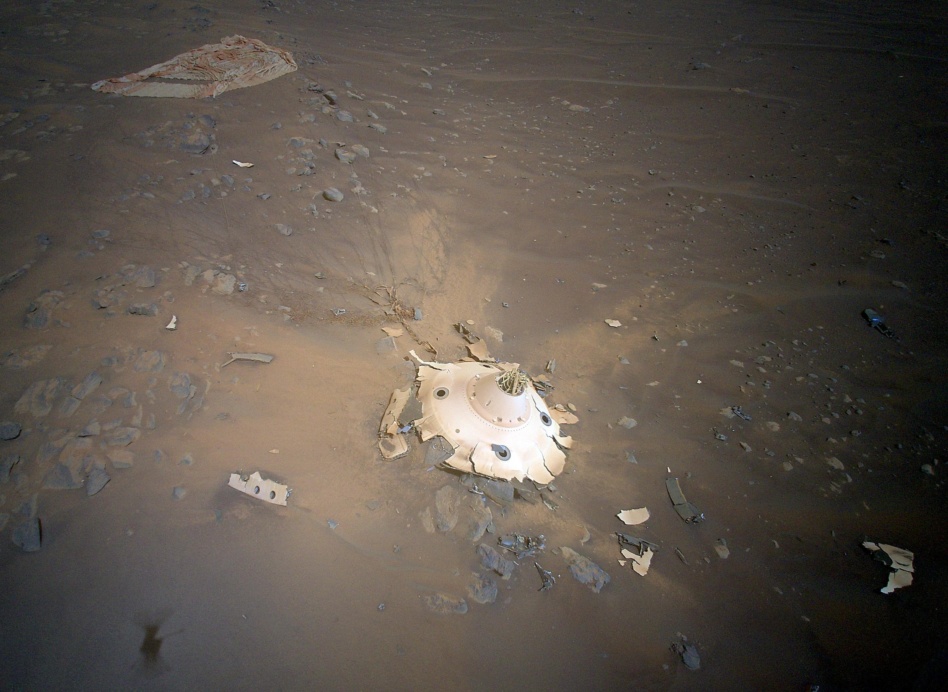
During its 26th fight, the Mars Ingenuity helicopter snapped incredible images of the parachute and backshell that helped the chopper and the Perseverance rover to land on the Red Planet’s surface a little over a year ago.
This was no coincidence: NASA and JPL intentionally directed the helicopter over to the landing site, thinking that photos of the landing debris could help ensure safe future landings for other spacecraft.
Ingenuity has had an incredible run on Mars so far. The craft was only originally meant to fly five sorties to validate whether or not flying in the planet’s thin atmosphere would even work. It does, and now the NASA Ingenuity team is using it to provide a different vantage point of the Martian surface.
A picture speaks a thousand words
Back at home, NASA scientists are analyzing the image of the parachute and backshell, which protected Perseverance during landing. The image shows some damage to the backshell, but it looks like the protective coating on the shell remained intact during landing, not destroyed by entering Mars’ atmosphere.
- The parachute and the lines connecting it to the backshell also look in good condition.
- Over the next few weeks, the team will continue to look for clues in the Ingenuity images.
A flying guide: Perseverance is headed to the Jezero delta to search for signs of microbial life. When it arrives there, researchers may use Ingenuity to determine what the rover’s best path should be to get to the top of the delta.