Startups
Stories about the new players changing the space game.
Lux Aeterna Closes $10M Seed to Build Reusable Sats
Everybody loves a reusable rocket—so why has the rest of space hardware remained stubbornly single-use?
Seraphim Space Investment Trust Posts Record Results
Seraphim Space Investment Trust ($SSIT) announced its financial results for H2 2025, revealing a successful portfolio of global space businesses that have seen valuations buoyed by geopolitical trends.
Exclusive: Starpath Unveils New Ultra-Thin Space Solar Panels
The panels are just 73g per square meter, and are priced around $15 per watt.
Austria Commissions its First Military Sat
Austria is prepping to launch its first military-commissioned satellite to fight a growing, invisible threat—interference with satellite navigation.
ISPTech Raises €5.5M to Scale Green Propulsion Tech
Green energy is all the rage in Europe, and the trend is beginning to reach beyond the stratosphere.
Phantom Space Acquires Vector Launch Assets
Phantom Space just got a boatload of pre-owned toys to play with.
Exclusive: Charter Space Launches an Insurance Brokerage
Charter Space is done dipping its toes in the insurance market—opting instead to cannonball in.
Sophia Space Raises $10M for Build Orbital Data Center Tech
Orbital data centers are closer to reality than you might think.
Remondo Unveils Plans for Sub-30 cm Resolution Sat
The company believes it can eventually build, operate, and launch each sat for $2M or less, according to CEO Ido Priel.
NASA Authorization Could Kick Start Space Nuclear Power
The fate of the NASA authorization bill being considered by Congress now could be a make or break moment for the budding space nuclear power sector, according to one company.
Deep Space Energy Pockets €980K to Build European Space Nuclear Power
The Latvian nuclear power startup is working on a solution for lunar missions hoping to survive the lunar night—a harsh, cold stretch of darkness lasting 14 Earth days that’s a death sentence for solar powered missions.
Univity Adds Direct-to-Device Service in VLEO Constellation
The company’s original vision was to deploy a 1,500 sat VLEO constellation to provide high-bandwidth connectivity for telecom providers. It’s now working to offer connections directly to consumer devices as well.
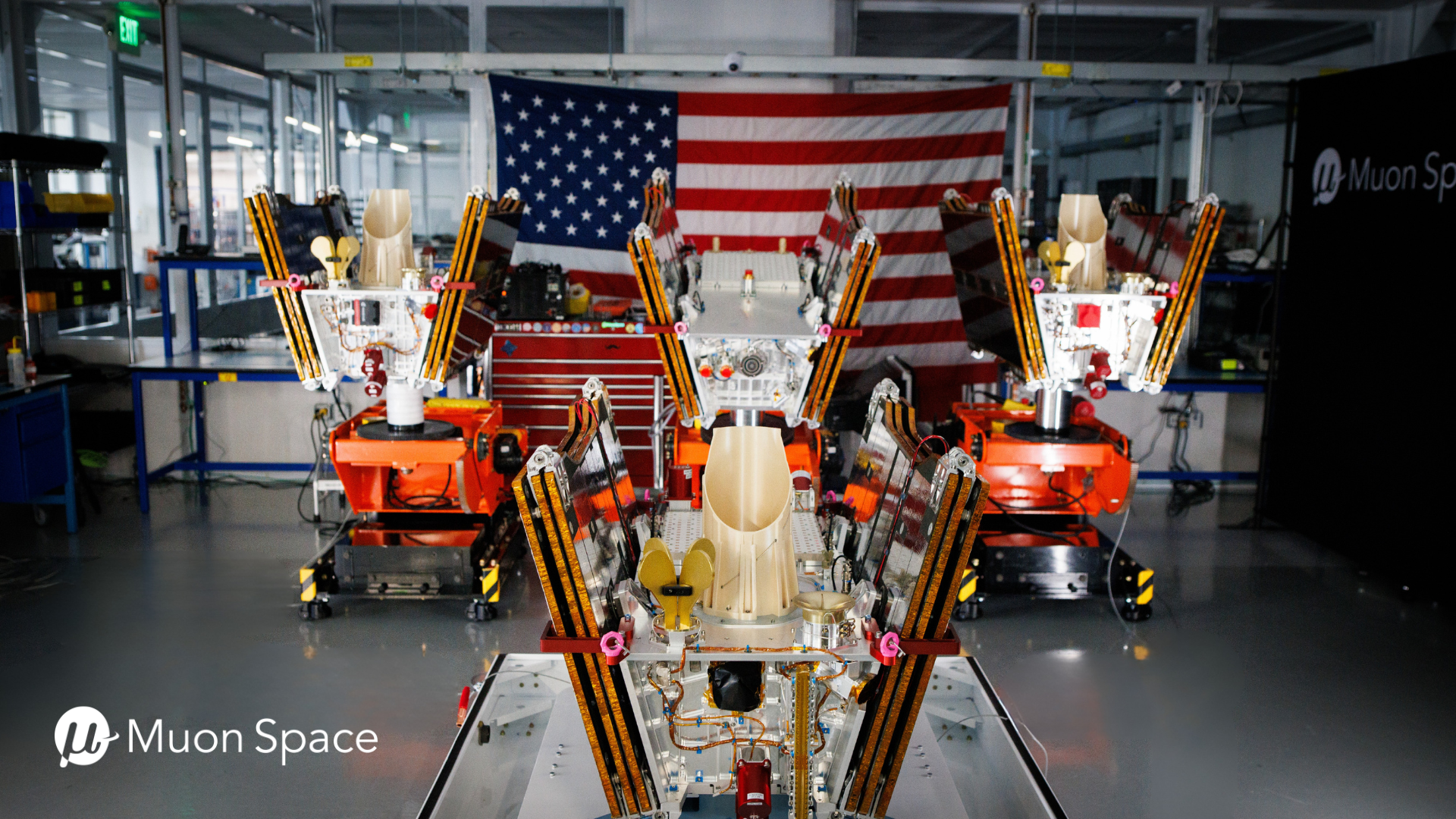
Muon Space’s Sat-Backed Growth Strategy for 2026
Muon has 20 satellites manifested to launch in the next 20 months, and expects more contracts to close in the coming year, according to CEO Jonny Dyer.