Beijing is increasingly using its space ambition to build a global coalition of international partners in orbit, according to a Pentagon report released last week.
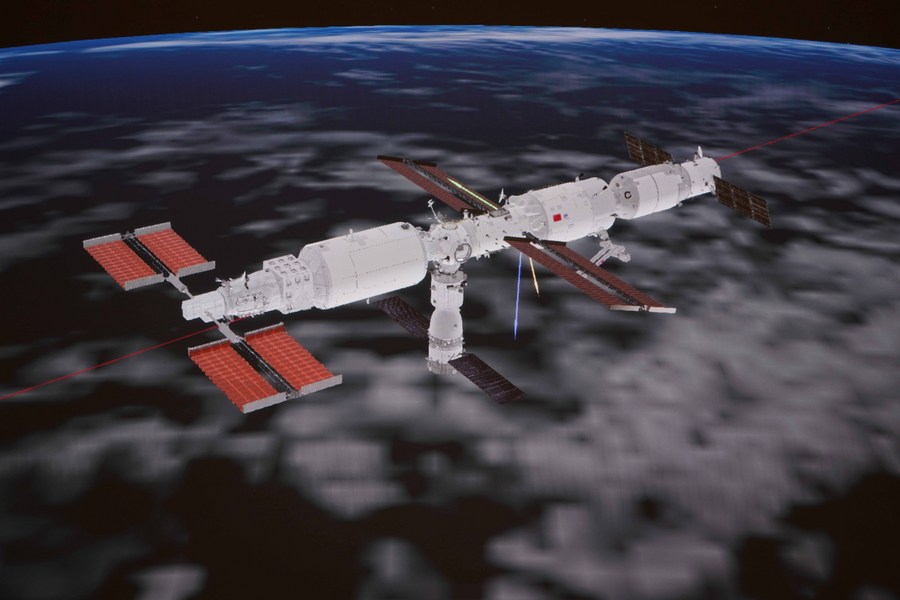
Better together: The China National Space Administration (CNSA) oversees China’s civilian space efforts, including plans for its own space station and the effort to build a lunar base in collaboration with Russia. The agency is also helping Beijing with its own brand of space diplomacy, according to the DoD’s 2023 China Military Power report.
“The PRC is increasingly using CNSA efforts to bolster relationships with countries around the world, particularly with the BRI Partners, providing opportunities to cooperate on space issues,” the report said.
Partners by the numbers: China already boasts 100+ cooperative space-related agreements with more than three dozen countries, according to the report. Some high-profile partnerships include:
- In October alone, three countries—Pakistan, Azerbaijan, and Belarus—have signed onto the International Lunar Research Station project, which is being led by Beijing and Moscow. Venezuela and South Africa are also partners on the ILRS.
- Researchers from non-ISS nations, including Switzerland, India, and Mexico, will send science experiments to the Tiangong space station under the United Nations Access to Space for All program.
- Beijing is also seeking to expand cooperation on space programs with Gulf nations, including Saudi Arabia and the UAE.
Fine line: While these partnerships are all on civil space programs, China maintains little-to-no separation between its civil and military priorities in orbit, according to the report.
In the military domain, China is continuing development of weapons in orbit, including direct-ascent anti-satellite weapons, co-orbital satellites that can surveil space assets, and directed energy systems, according to the Defense Department.
“The [People’s Liberation Army] views space superiority, the ability to control the space-enabled information sphere and to deny adversaries their own space-based information gathering and communication capabilities, as critical components to conduct modern ‘informatized warfare,’” the report said.