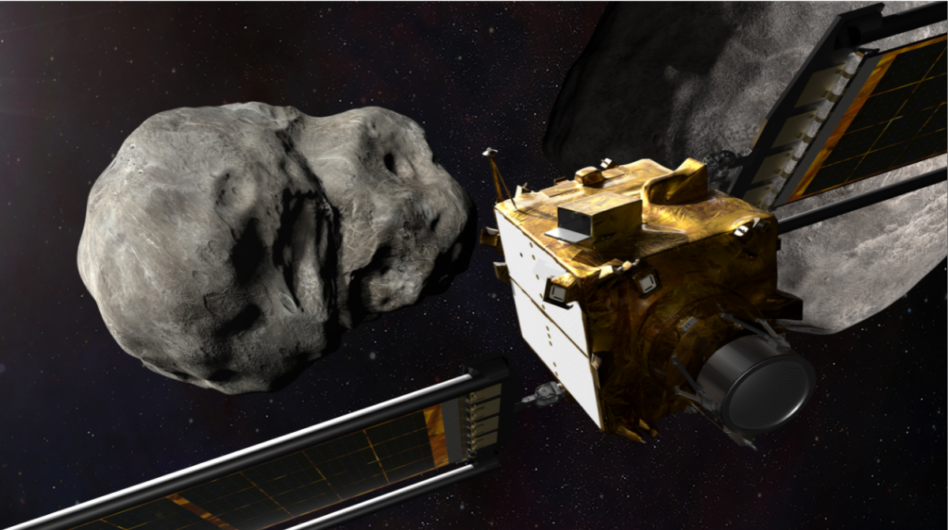
NASA is set to launch its Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket on Wednesday. The mission will slam a spacecraft into an asteroid, hoping to knock it slightly off its orbit.
A bit more detail: NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office contracted the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) to build DART. APL has a history of building guided missiles for the US military. NASA, meanwhile, wants to test if a guided craft can hit an Earth-threatening asteroid hard enough to derail it. It’s a match made in heaven.
APL built a few new technologies into the DART mission:
- The craft will drive itself using Small-body Maneuvering Autonomous Real-Time navigation.
- Its eyes = the Didymos Reconnaissance and Asteroid Camera for Optical Navigation.
- The Deployable Space Systems Roll-Out Solar Arrays are making their deep-space debut.
- “Kinetic impact deflection,” aka “hit it and make it move.”
The bullseye: DART’s target is Dimorphos, which, at a ~525-ft. width, dwarfs the cubic, four-foot wide, ~1,210-pound DART spacecraft. Were a similar-sized asteroid to hit Earth, it could send humanity the way of the dinosaurs.
NASA scientists will monitor the impact via telescope to determine the feasibility of this technology. We hope it works—and that they never have to use it.