The UN’s 26th UN Climate Change Conference—or COP26—has started in Glasgow, Scotland. On the docket: decarbonization negotiations. Over 120 world leaders will gather in Glasgow over the next week.
- FYI: In its latest climate science report, published in August, the UN calls for the world to limit warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
What’s space got to do with the Scottish talks?
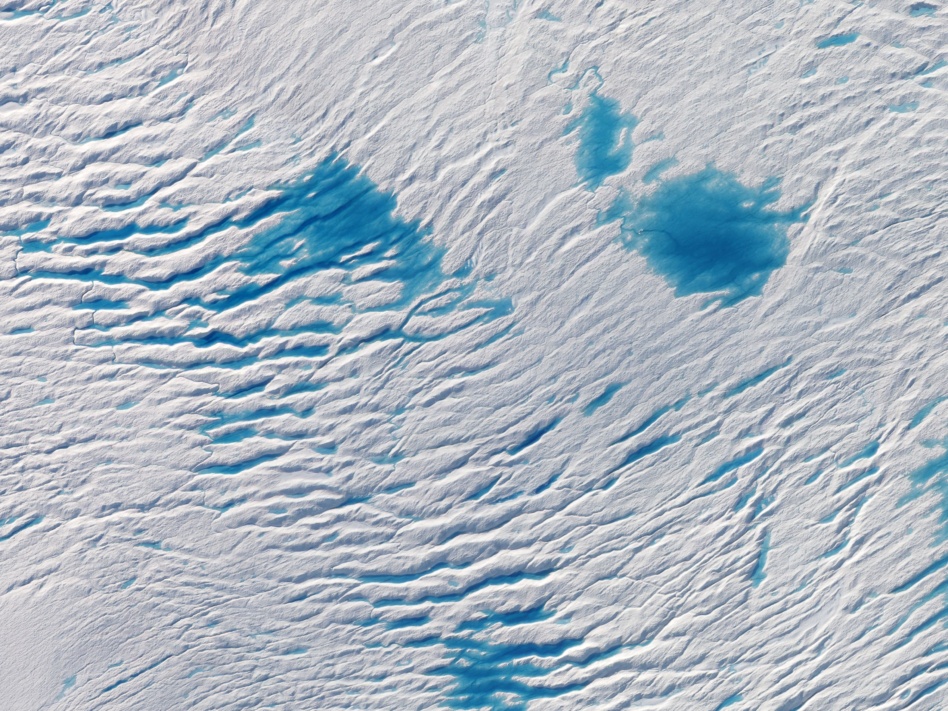
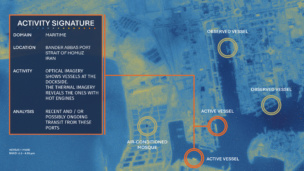
Well, satellite-gathered data is pretty central to our understanding of how the planet is changing. Earth Observation (EO) is one of space’s most commercially advanced—and competitive—sub-sectors. EO imagery is indispensable in tracking climate change and contributing to mitigation strategies.
It’s no surprise, then, that EO players have made their way to Scotland for COP26 (including Satellite Vu, a UK company we recently spoke with).
The Group on Earth Observations (GEO), a partnership of 100+ governments and organizations, will participate in negotiations and dozens of COP26 events. The group’s goals in Glasgow are to “promote the role of EO” in climate solutions.
The long view: “Satellites were absolutely key in understanding we had a climate crisis,” Krystal Azelton, director of space applications programs at the Secure World Foundation, told Politico.
By the numbers:
- The White House’s first annual budget proposal sought $24.8B for NASA, including a $2.25B for the Earth Science Division, and $6.98B for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
- Those numbers would represent annual boosts of 12.5%, 22%, and 25%, respectively. Expect final numbers to be slightly lower, though, once congressional appropriators are all said and done.
- Hundreds of commercial EO satellites are in low-Earth orbit (LEO).
+ Want more? Read Politico’s excellent deep dive published yesterday, on how EO constellations could help us “wage war” on climate change. Also check out Quartz’s article on finding hidden emissions with satellites.