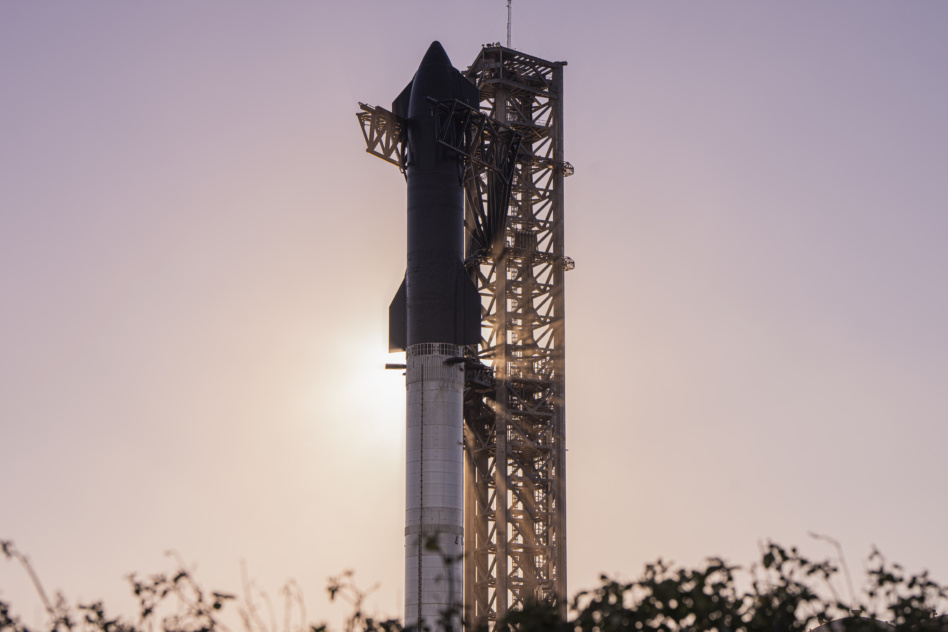
The FAA is planning an Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) to assess SpaceX’s proposed modifications for Starship operations at KSC site LC-39A.
The review is considering up to 44 Starship launches at the site each year.
Make room for Starship: SpaceX has used LC-39A since 2014 for Falcon 9 and Heavy launches. NASA already completed the less cumbersome Environmental Assessment (EA) of potential Starship operations at LC-39A in 2019, which evaluated the impact of a new Starship launch pad build-out and a 24-launch-per-year manifest.
Post-approval, SpaceX began Starship infrastructure construction.
However, the company’s Starship operations have changed substantially since the original EA, and the agency determined that a new, broader EIS assessment was warranted to evaluate whether the operations would negatively impact the biological or physical environment.
What’s new?: The new Starship infrastructure requests include:
- A water deluge system
- Propellant storage
- The ability to employ nine engines for its Starship second stage and 35 engines for its booster, up from the six and 33 engines that are currently used
- A catch tower equipped with metal arms that can swing close and secure a hovering Starship vehicle in midair, enabling reusability
EIS reviews are thorough and typically take north of a year to complete. The agency is opening public scoping hearings next month.
Back at Starbase: SpaceX aims to launch Starship on flight 4 in three to five weeks. At a recent Starship presentation, Elon Musk said it may also attempt the daunting tower catch at Starbase on flight 5.
+ FAA learning period: The Senate passed the FAA reauthorization bill on Thursday, which extended the commercial human spaceflight learning period until Jan. 1.