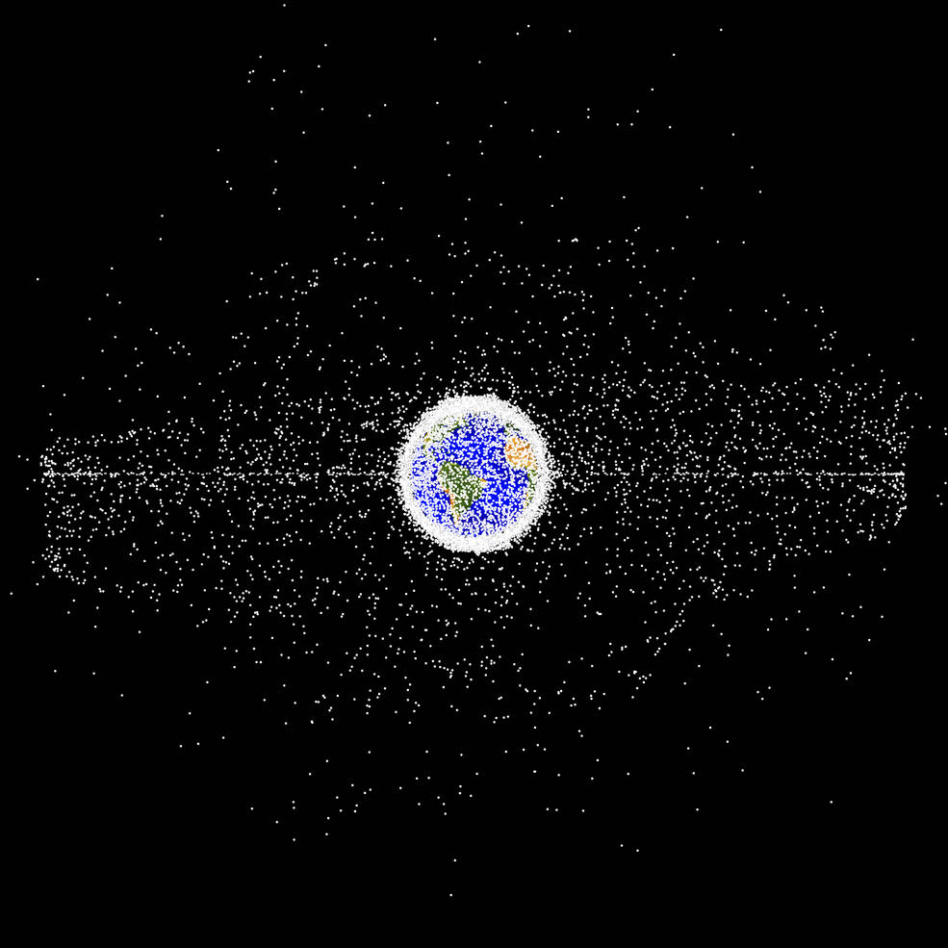
The European Space Policy Institute (ESPI) published an analysis of the global efforts to mitigate the proliferation of space debris yesterday.
In the report, the institute found that space debris mitigation efforts from governments, NGOs, and companies are gaining steam.
- International efforts to address the risks posed by the increasing volume of space debris have expanded in recent years.
- The scope and stringency of these efforts have also increased, with better adherence to generally accepted space debris mitigation goals.
- While the international community has yet to agree on a single set of rules, different initiatives share similar goals and frameworks.
- The report recommended that international bodies align their space debris mitigation goals so they can implement concrete rules and best practices globally.
Same, same, but different: ESPI analyzed 15 different instruments that have been created since the turn of the millennium to demonstrate momentum growing in the international space sustainability movement.
From the first IADC Space Debris Mitigation Guidelines published in 2002 to ESA’s Zero Debris Charter in 2023, these efforts have varied in their content and structure, but over time they have grown sharper teeth, the report said.
In Europe especially, the laws and guidelines governing space debris—ESA’s Space Debris Mitigation Requirements and the Zero Debris Charter—cover a large number of countries, and include concrete commitments and specific methods to monitor compliance.
Upcoming regulation: There are signs that the patchwork set of regional sustainable regs is primed to come together.
On Sunday, the UN General Assembly adopted the Pact for the Future, which included a commitment to prevent an arms race in space, and an agreement to strengthen the international framework for sustainable practices.
This agreement promises more discussion about a tangible international framework on the specific methods of debris mitigation. However, in the short-term, it reaffirms the “widest possible adherence to and full compliance with the 1967 Outer Space Treaty.” Not a bad place to start.