Intelligence agencies have their own tactics and techniques to follow the latest military developments near Ukraine. But spies aren’t inclined to share all that classified information with the rest of us.
Satellite imagery, along with other sources like social media posts and video geolocation/metadata, enable open-source intelligence (OSINT) analysis from publicly available data. Coupled with extra legwork from analysts, reporters, and open-source sleuthers, this data means that anyone who wants to follow along doesn’t need to be left in the dark.
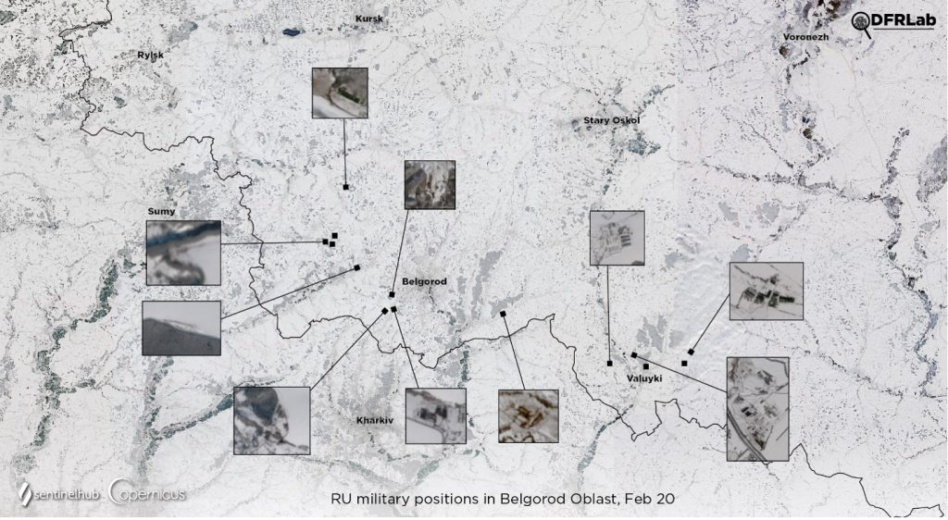
The space angle: Commercial satellite imagery in particular has made it impossible for Moscow to conceal a military buildup in Belarus and forces massing near Ukraine’s border in recent weeks. Reuters, the BBC, the NYT, and countless other newsrooms have tapped a glut of imagery from space to track the latest developments nearly in real-time.
- One Maxar image from Monday, for example, shows field tents set up after Feb. 5 that are roughly seven miles from the Ukraine border. Other images show a recently established field hospital and activity ramping up at an aerodrome in Belarus.
- Analysts have also tapped satellite images to track land clearing, equipment transporters, troop movements, and aircraft deployments.
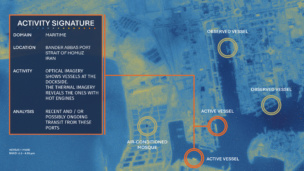
- Capella Space has supplied synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imagery in recent weeks that shows the forward march of Russian military forces. With SAR, “seeing” through wintry conditions/cloud cover and following ground-level changes is no problem.
It’s not just commercial Earth observation (EO) companies or proprietary datasets that can come in handy in the OSINT department. Researchers this week also referenced heat-sensing and wildfire data from NASA to cross-check FSB claims. And the Atlantic Council, a DC think tank, has used ESA satellite data to track military positions in recent weeks.
Reality check: Commercial satellite imagery has enabled those with the know-how to essentially become intelligence analysts, no security clearance needed. What was once private can now be shared for the world to see in plain sight.
As Axios recently put it, “the images are showcasing the abilities of Earth observing satellites that are often marketed as climate intelligence platforms, but in reality are also used for less advertised national security purposes.”
- And…“The primary source of funding for nearly all of these, all of the commercial satellite imagery sector at the moment is the national security community,” the Secure World Foundation’s Brian Weeden told Axios.