This week, Sens. Maria Cantwell (D-WA), John Hickenlooper (D-CO), Cynthia Lummis (R-WY) and Roger Wicker (R-MS) introduced the Orbital Sustainability (ORBITS) Act on the Congress floor. The bipartisan bill is aimed at developing active debris removal (ADR) technology, with the eventual goal of removing dangerous debris objects from orbit.
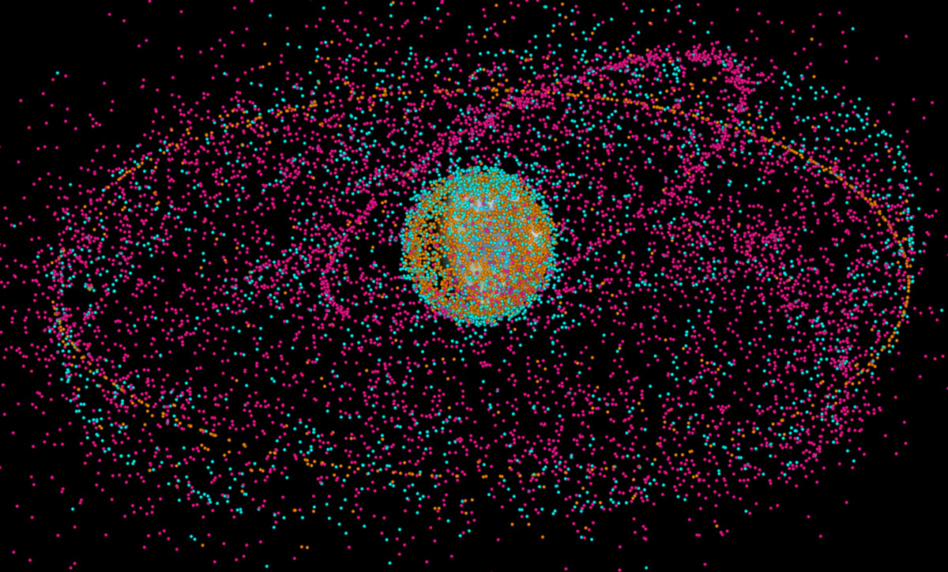
The debris problem: 100M+ individual pieces of debris are in Earth orbit right now, ranging from flecks of dust and paint to spent American and Soviet boosters to decommissioned, defunct satellites. As the space industry gears up to launch tens of thousands of satellites in the coming decade, spacefaring nations’ governments are figuring out how to stop the dreaded Kessler syndrome before it becomes a reality.
Orbital debris is notoriously difficult to regulate. So far, humans have yet to actively remove debris from orbit. While rapidly advancing, ADR is far from the promised land of commercial viability.
“With any new technology, government investment in R&D is essential,” Chris Blackerby, COO of Astroscale, told Payload a few months ago. Public investment can help get innovative new ideas, like ADR, over the “valley of death.”
- For its part, the US Space Force plans to “prime” ADR and other on-orbit servicing technologies by kickstarting market incentives and helping fund demoes.
Draft legislation
The ORBITS act spans four pillars. The bill would:
- Direct NASA, the Office of Space Commerce (OSC), and the National Space Council (NSpC) to create a list of the most dangerous pieces of debris in orbit
- Direct NASA to create a program focused on debris removal R&D
- Update orbital debris mitigation guidelines across multiple government agencies
- Require OSC, the National Space Council, and the FCC to develop practices to improve space situational awareness and space traffic management.
The second provision would allow NASA to petition industry for ADR demonstrations, a major step for advancing this technology in the US. The bill recommends appropriations of $150M from 2023 to 2027.
+ While we’re here…Orbital debris mitigation is top-of-mind across US government agencies. Yesterday, NASA announced funding for three research proposals on the topic of space sustainability, focusing on the economic, social, and policy impacts. The three awardees:
- Richard Linares and Danielle Wood from MIT and Moriba Jah from UT Austin
- Akhil Rao from Middlebury College, Daniel Kaffine from the University of Colorado-Boulder, and Brian Weeden of the Secure World Foundation
- Patrice Kohl, Sergio Alvarez, and Philip Metzger of the University of Central Florida