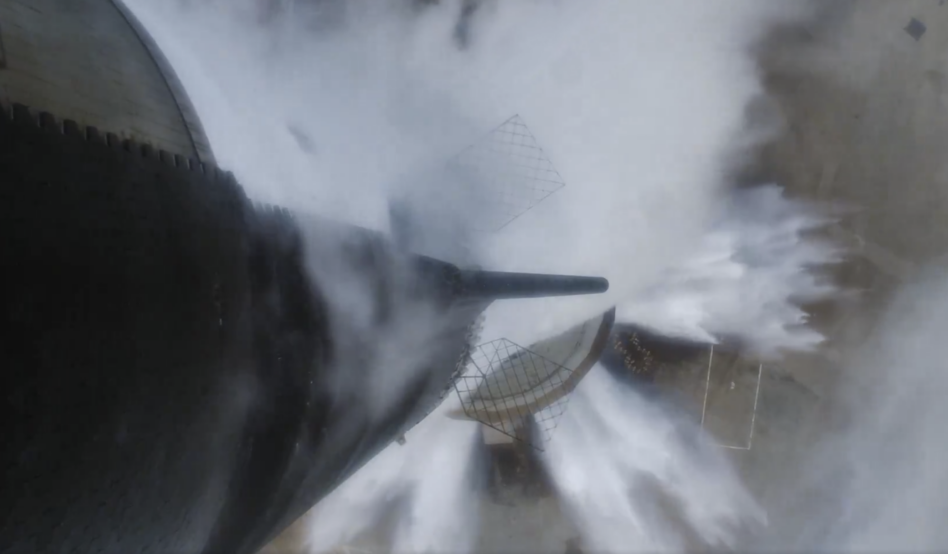
Texas and federal officials have both reportedly found that SpaceX violated environmental regulations discharging wastewater at its Starbase facility.
SpaceX responded to the reports, saying that state and federal regulators gave it permission to continue operating its deluge system while it worked towards getting the appropriate permits. TCEQ and the EPA had not confirmed waiving the permit requirements as of press time.
The latest development in SpaceX’s long-running struggle with environmental regulations at its Boca Chica launch site was first reported by CNBC. SpaceX purchased land on the Gulf of Mexico in 2014 and has developed it to host the development and launch of Starship, its next generation rocket.
Why wastewater matters: SpaceX won FAA approval for regular launches from the site in 2023—so long as the company met standards set out by various agencies, including rules designed to limit the environmental impact of launches.
After Starship’s first test flight in April 2023 damaged the launch pad, SpaceX built a deluge system that dampens the energy from Starship’s 33 Raptor engines, releasing 422,000 gallons of water per flight, much of which is immediately vaporized.
Monday’s news suggests more delays ahead as the company seeks to win approval not just for its next launch, which was expected as soon as September, but also for a higher launch cadence. Yesterday, the FAA suddenly postponed a series of public meetings to discuss increasing launches and landings at Boca Chica.
“The FAA is seeking additional information from SpaceX before rescheduling the public meetings,” the agency told Payload in a statement.
SpaceX says: The company posted a statement on social media that stressed the company’s efforts to comply with environmental rules, including only using clean water in the system. However, SpaceX filings say ablation of its launch structure can contaminate the water, and a Texas ecologist told CNBC that mercury measurements by the company concerned him.
SpaceX submitted its request for an individual permit to the Texas Council on Environmental Quality on July 1, about a year after installing the deluge system.
Arpita Dasika contributed to this report.