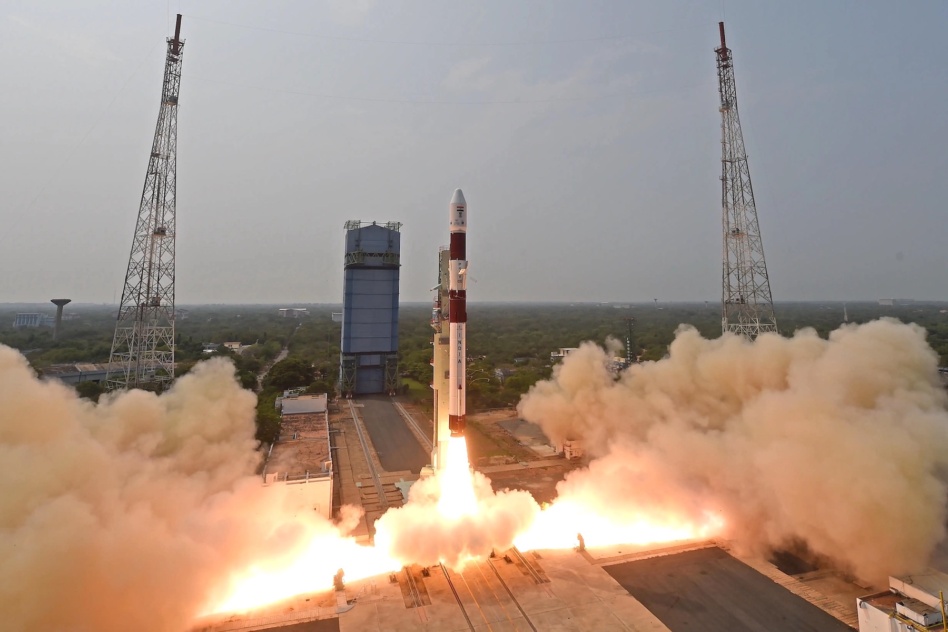
Cubesats may soon be able to find their way in space at a lower cost thanks to a new star sensor developed by Indian researchers, which launched to space on Saturday.
Starberry-Sense hopes to help small satellites determine their orientation in space in relation to surrounding stars for just 10 percent of the cost of currently available commercial options, which can cost more than an entire cubesat, says the Indian Department of Science and Technology.
The 470-gram module, which was developed by researchers at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics, is powered by a Raspberry Pi Zero computer. The demo mission is expected to last three to six months.
A modified Starberry-Sense will be utilized in the Indian Astronomical Observatory at Ladakh.
What else is on board
The ISRO PSLV rocket launch also deployed two commercial payloads for Singapore: the TeLEOS-2 synthetic aperture radar satellite and the LUMELITE-4 smallsat, a maritime-related technology demonstrator.
TeLEOS-2, which was developed by Singapore’s domestic space industry, can do fully polarimetric radar imaging at 1-meter resolution. It’s the country’s second Earth observation satellite; the first, TeLEOS-1, launched aboard a PSLV in 2015.
A focus on reusability
The launch is the third time ISRO repurposed the PSLV’s fourth stage as a stabilized, solar-powered platform for onboard payloads. This affords organizations low-cost access to space for demonstrating their technologies ahead of use in future missions. ISRO calls the platform the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module, or POEM. The Starberry-Sense module is mounted on it.
On this launch, POEM is home to seven payloads, notably including an ionospheric analyzer and a privately developed Hall-effect thruster. In a post-launch briefing, ISRO officials said this POEM is the first to sport deployable solar panels, which increases its power generation capacity from 150 watts to 500.
Ramping up
The PSLV that launched on Saturday was integrated at ISRO’s new namesake facility near the first of the two launch pads at Sriharikota. The PSLV Integration Facility cuts down assembly time by several weeks, enabling ISRO to launch a PSLV a month. At the same time ISRO and NSIL are working on increasing PSLV’s production rate by having them fully built by industry as part of a $104 million contract awarded to a consortium of major PSLV contractors.