The space industry thrives on continuous hardware innovation and the advancement of materials designed to withstand the harshest conditions imaginable.
The Niobium C103 refractory alloy is a prime example.
Refractory alloys stand out in aerospace and defense applications due to their ability to maintain their structural integrity and mechanical properties at extremely high temperatures. Comprising 89% Niobium, 10% Hafnium, and 1% Titanium, Niobium C103 has emerged as a game-changer in the refractory alloy domain.
Niobium C103 parts that are additively manufactured (AM) boast nearly double the strength and orders of magnitude higher creep resistance at elevated temperatures compared to the wrought alloy.
These characteristics allow it to significantly outperform other materials in the unforgiving environments of launch and space applications, where extreme temperatures—which can be above other superalloys’ melting points—and strong erosive conditions are the norm.
- Strong: AM Niobium has a tensile strength of over 70 ksi and is better able to maintain strength as the application temperature increases. This has made it a go-to choice for aerospace components and missile casings that must endure high stress without failure.
- Lightweight: Niobium is among the lowest density refractory alloys. High strength-to-weight ratio translates to lighter components, enhancing fuel efficiency and payload capacity.
- Temp resistant: The alloy can withstand temperatures exceeding 3,300 degrees Fahrenheit, positioning it as an ideal candidate for rocket and spacecraft nozzles, injectors, and hypersonics.
Diving into Niobium C103 use cases:
Thrusters/Nozzles/Injectors: Rocket propulsion systems demand materials that can handle extreme heat during launch. When regenerative cooling isn’t feasible or simplified component designs are needed, AM Niobium C103 presents a compelling material for engine components.
Furthermore, propulsion systems designed for deep space exploration can leverage Niobium C103 to create lighter components capable of withstanding the challenging lunar and deep space environments.
- SpaceX’s upper-stage Merlin engine nozzle extension and Dragon capsule reaction control engines use traditional Niobium C103.
Hypersonics: Hypersonic missile tech is front and center in next-gen defense tech. On the commercial side, companies like Hermeus aim to make hypersonic passenger travel a reality in the coming years. Hypersonic aircraft and missiles operate at speeds that can exceed Mach 5, exponentially increasing the temperatures they must withstand. The exceptional strength and resilience of AM Niobium C103 in such conditions make it the go-to material choice for non-ablative sharp leading edge, nose cone, and control surfaces.
General thermal management: Managing heat is critical in many high-tech applications, including satellites and planes. AM Niobium C103’s capabilities make it invaluable for components ranging from cold plates to heat sinks, heat exchangers, and battery cell components.
Enter Castheon:
Castheon has emerged as a trailblazer in the space industry, showcasing its commitment to innovation through specific programs involving Niobium C103. Collaborating with NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center, (US Air Force, and AFRL, DARPA) the company has contributed to groundbreaking research and production of AM C103 green propulsion thrusters and stand-off technologies, pushing the boundaries of propulsion systems for space exploration.
The versatility of Castheon’s Niobium C103 is evident in its adoption by industry leaders such as Benchmark Space Systems, where it has been utilized for both Lynx and Ocelot thruster assemblies in space flight applications. Additionally, the company’s partnership with Firefly Aerospace extends to the production of Niobium combustion chambers for their Moon lander, highlighting Castheon’s integral role in advancing cutting-edge space initiatives.
Manufacturing Niobium: Refractory alloys require high-cost and complex manufacturing processes, historically limiting their applications. Castheon has tackled these challenges by developing Niobium C103 refractory additive manufacturing tech. Leveraging additive manufacturing, components can be an order of magnitude more cost-effective and manufactured ten times faster, all while exhibiting robust strength and durability at hypersonic temperatures.
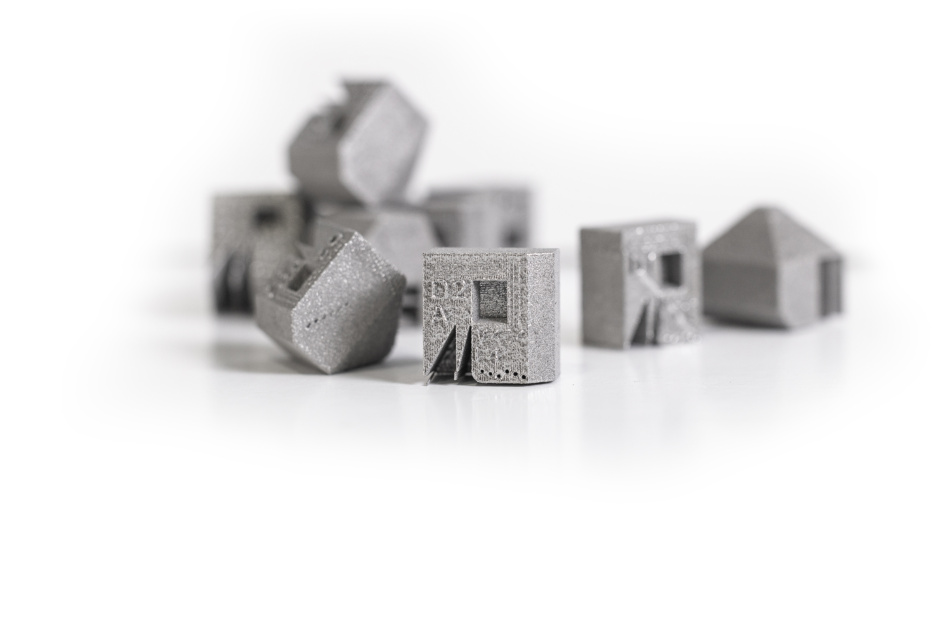
The Gao Block: a catalyst for innovation: Central to Castheon’s innovation journey is the Gao Block, a unique test part conceptualized and developed by the company’s founder and chief scientist, Dr. Youping Gao.
- This intricate and simple geometric part unlocks an array of challenging features, including overhangs, undercuts, and fine details, making it a powerful testing tool for 3D printing.
- The Gao block allows Castheon’s research and development team to test and optimize new metal additive processes and parameters rapidly to deliver metallurgically sound materials with optimized grain structures.
- These parameters include laser power, scanning speed, and layer thickness, all crucial for achieving the desired quality and consistency of parts.
Positioned for a manufacturing revolution: Castheon is not just a solitary entity but part of the ADDMAN Group, a broader business offering a complete range of manufacturing services. This affiliation empowers Castheon to provide its customers with comprehensive solutions, from initial design concepts to the end of a product’s life cycle. Integrated within the ADDMAN Group, Castheon seamlessly combines polymer 3D printing, injection molding, traditional manufacturing services, and cutting-edge metal additive capabilities. This consolidated approach makes Castheon a one-stop shop for all manufacturing needs, ensuring efficiency, precision, and innovation at every stage of the process.
By investing significantly in cutting-edge technology and research, Castheon is strategically positioned to lead a revolution in the manufacturing of high-performance space components.