Ursa Major received a contract from the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) on Tuesday to test a prototype of its new Draper engine for hypersonics and to continue developing its Arroway engines.
AFRL awarded these funds aiming to decrease US dependence on foreign propulsion systems for space launch, a key goal of its rocket propulsion division.
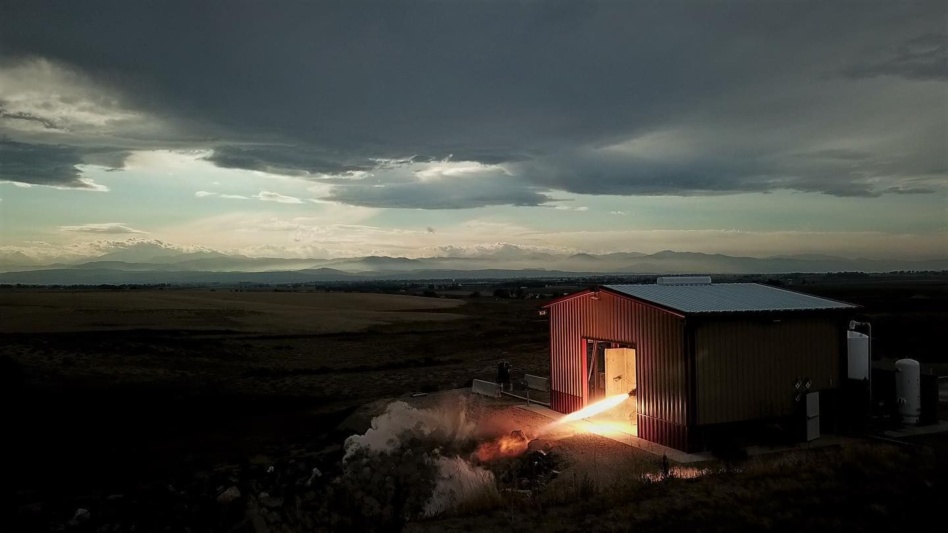
The Draper engine: As part of the contract announcement, Ursa Major revealed Draper, which is designed to defend against hypersonic weapons. The 4,000-pound thrust engine is designed for hypersonic applications, and its fuel, a hydrogen peroxide and kerosene blend, is storable, optimizing the design for rapid-response and launch on demand.
- The startup claims that solid rocket engines cannot offer the same degrees of maneuverability and flexibility required by missile defense systems.
- A hotfire test is planned within 12 months.
The Arroway engine: Ursa Major unveiled its Arroway engine, a 200,000-pound thrust reusable liquid oxygen and methane engine for medium and heavy launch vehicles, in August 2022. When several of these engines are clustered together, they will be capable of supporting next-generation heavy launch vehicles.
Payload’s takeaway: Over the past few decades, the US defense industrial base has consolidated drastically, leaving behind only two independent propulsion providers by 2020. The DoD’s push for a stronger base of domestic propulsion providers—as well as a hunger to develop homegrown hypersonics capabilities—has led to a broader field of competition in the rocket engine manufacturing space.