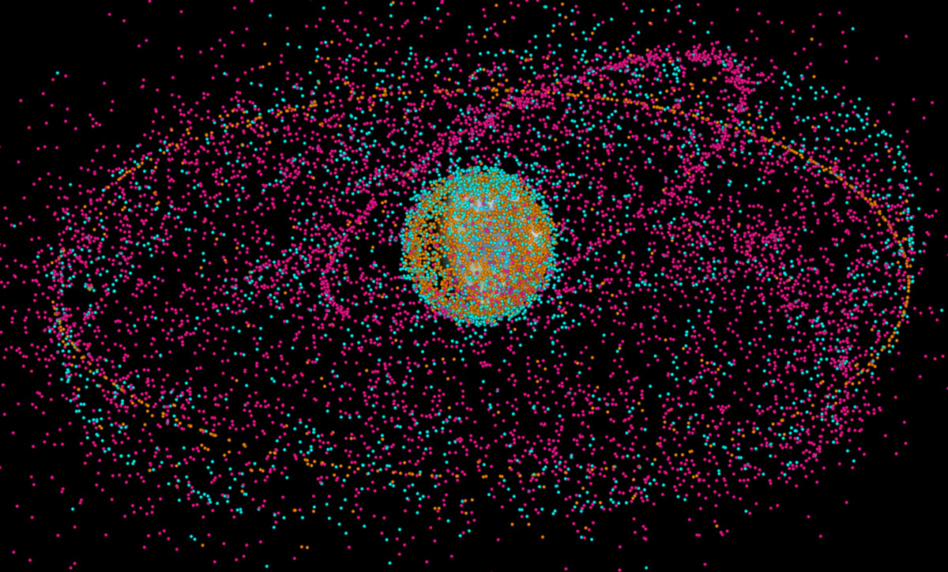
The White House has decided it’s time to do something about space junk. On Friday, the National Science and Technology Council released a 44-point national orbital debris implementation plan that aims to nip the littering problem in the bud before it threatens the safe operation of satellites in orbit.
Multiple US agencies are currently involved in some aspect of orbital debris management, with NASA, the FAA, the FCC, the DoD, and the DoC each pulling a different set of strings. The new implementation plan divides responsibilities between the agencies to improve debris prevention, tracking, and removal.
Leave no trace
The first pillar of the plan, debris mitigation, is aimed at minimizing the amount of junk that ever actually gets to orbit. Ending debris creation is, in the long term, the best way to keep the orbital environment trash-free and safely operable.
The steps:
- Research where in the launch process debris creation occurs, and offer incentives to address those pain points
- Develop best practices for debris mitigation and educate the satellite operator community on them
- Implement shared rules of the road for deconfliction maneuvers
- Design add-on devices for satellites, including propulsion or other deorbiting mechanisms, to minimize collision risk.
- Revisit deorbit guidelines, which currently maintain that operators in LEO must deorbit their satellites after 25 years.
Eyes on the sky
Pillar #2, tracking and characterization of debris, lays out steps for improving our observation capabilities for tracking spacecraft and debris in orbit.
The steps:
- Improve our knowledge of the space environment, including atmospheric density and environment models and space weather prediction
- Identify improvements for collision avoidance and conjunction assessment technology, which includes funding R&D in a wide range of fields
- Use the data from these studies to improve debris characterization models
- Provide a communication platform for government and commercial satellite operators to share data and report maneuvers.
Picking up the pieces
Last but not least, the debris implementation plan addresses technologies being developed to remove existing debris from orbit. Active debris removal (ADR), on-orbit servicing, and debris recycling are all considered under this pillar.
The steps:
- Figure out how much of a risk existing debris poses to spacecraft and estimate the cost of developing remediation tech
- Advance the technology readiness levels (TRL) of ADR and on-orbit servicing and refueling capabilities
- Look into the legal implications of ADR and close approaches in space under the Outer Space Treaty.
Upshot: The implementation plan is full of calls for discussion, collaboration, and R&D, but we aren’t going to be seeing any major changes in regulation in the near term. Shortening the current 25-year deorbit deadline and creating an open data sharing platform for satellite operators would each be major steps toward more responsible orbital stewardship. An influx of funding to increase the TRL for debris mitigation and removal would provide a path toward federal acquisition of these nascent technologies. So far, none of that is set in stone.
+ While we’re here: Check out Part 1 and Part 2 of our deep dive into orbital debris and what’s being done about it.