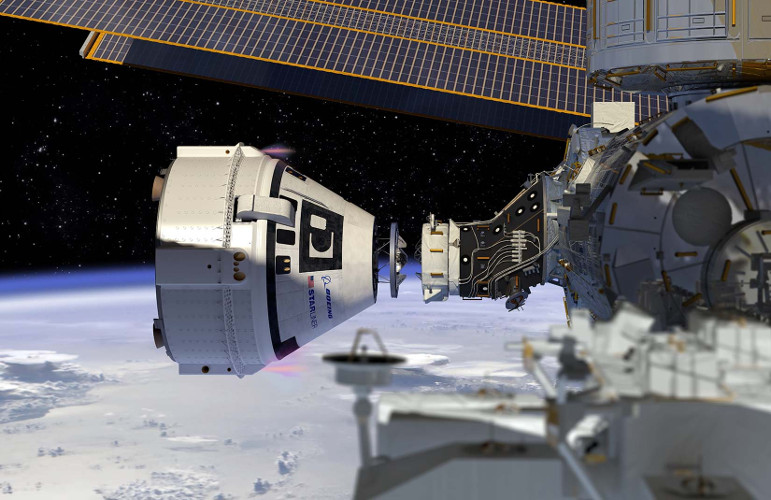
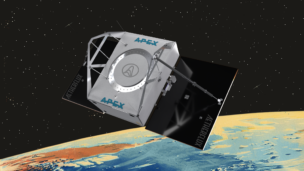
Starliner isn’t yet ready for a crew. Just a few weeks before the Boeing-built capsule was scheduled to deliver its first passengers to the ISS, NASA and Boeing leaders announced that two major issues with the craft will delay the first crewed mission even longer.
The announcement follows a review by NASA’s Aerospace Safety Advisory Panel last week, which warned against rushing into a crewed flight before all of Starliner’s potential safety concerns could be thoroughly investigated and addressed.
The issues: In reviews late last week, the Boeing team identified two issues with the Starliner craft that could cause disaster in certain flight scenarios:
- Parachutes. The soft links that run from the capsule to its parachutes aren’t as strong as they need to be. If one of the three chutes doesn’t deploy, the team found that it’s likely the links to the other two could snap.
- Tape. There are hundreds of feet of wiring harnesses strung throughout the vehicle, and these harnesses are wrapped up in a type of glass cloth tape called P-213. Recent tests showed that this tape might be flammable in certain circumstances.
Looking back: Boeing and SpaceX were selected at the same time in 2014 to build commercial crew transport vehicles to send astronauts to the ISS. Neither vehicle met the original target of flying in 2017, but SpaceX beat Boeing to the punch, launching its first crewed mission in 2020 (and nine others since).
Boeing has met many of the milestones for its $4.2B fixed-price contract already, having flown two test flights of Starliner so far.
Looking forward: Starliner won’t fly in July as previously planned. Boeing is spending this week figuring out exactly what needs to be done to get Starliner ready to fly again. The capsule will likely need to complete additional test flights before it can fly a crew. Boeing VP and program manager Mark Nappi declined to provide a timeline for the capsule’s first crewed mission until the team has completed its review.