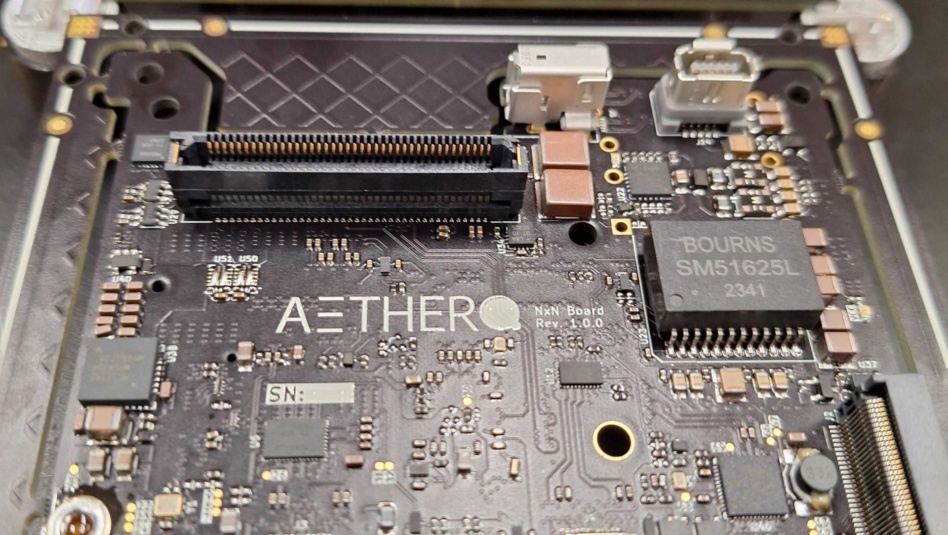
Aethero, a San Francisco space computing start-up founded by Edward Ge and Amit Pinnamaneni, revealed its business model after raising $1.7M in seed funding last year.
The five-person firm wants to bring high-performance processing to satellites. Existing spacecraft have some amazing capabilities, but they’re hitting a bottleneck when it comes to compute, and the next generation of space capabilities, such as orbital servicing, will require even brainier orbiting robots.
What’s the pitch? “[Satellite] processing power is still very primitive,” Ge told Payload. “Satellites still require a ton of people on the backend. There’s still a ton of latency of getting data down. And the software and the AI and ML applications that can run on board are very much limited. [If we] put more processing software onto these satellites, we can vastly increase the use cases they can tackle. We let them handle way more tasks by themselves without needing input from Earth. And just like that we will enable massive, massive growth of the space economy—ultimately we want to be that Intel that enables that.”
Origin story: Ge and Pinnamaneni are childhood friends who dropped out of University of Michigan undergrad and grad programs, respectively, to found Aethero in 2023. They first encountered the problem they aim to solve while developing a previous company, which aimed to build a remote-sensing balloon platform for customers like the National Geospatial Agency.
“The problem is getting data fast enough,” Ge said. Even after collecting imagery of a target, an Earth observation satellite could take hours to transmit the raw data to providers and then on to customers. “What we can do with edge computing in space is compress that data and process it instantaneously.”
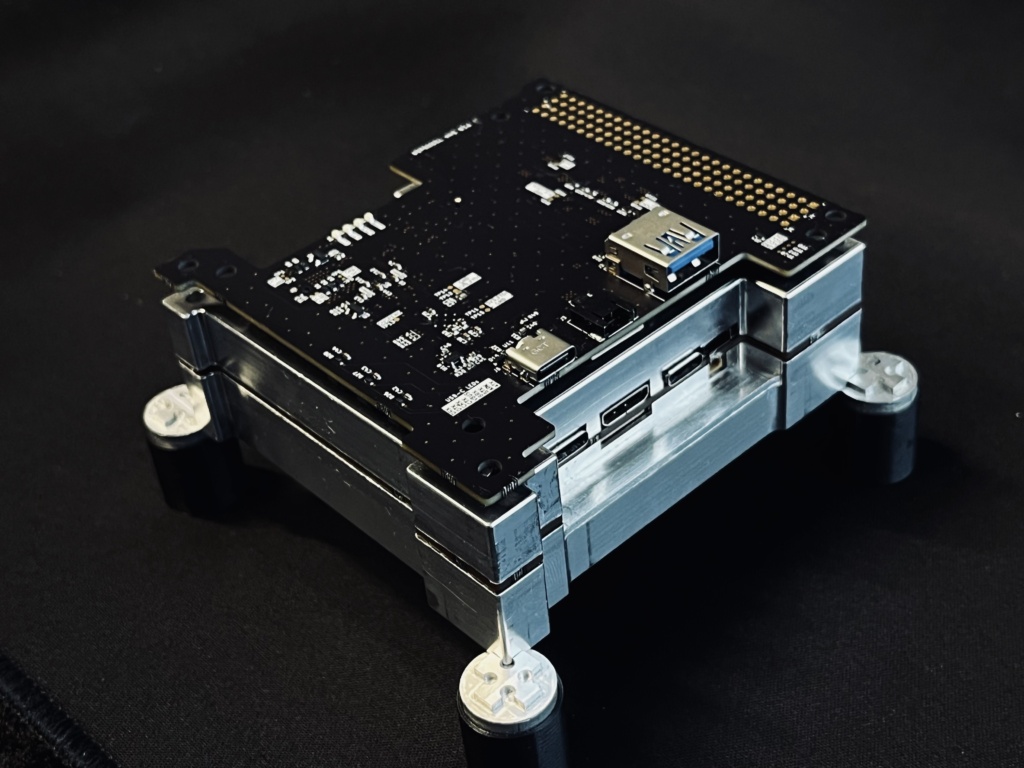
And as remote-sensing satellites increasingly use SAR and hyperspectral sensors, the data is only getting harder to manage. Widely used space computers today can deliver 5.3T operations per second, Ge said, while Aethero’s first generation product, AetherNxN, can perform 100T operations per second.
How it works: Aethero builds the radiation shielding and baseboard for its computers, and writes custom software to support space applications. Right now, it uses Nvidia’s Orin processors, but plans to develop a proprietary chip suited to machine learning applications after it gains traction in the market.
Though the company is launching a home-built demonstration satellite on an upcoming SpaceX Transporter mission, Aethero doesn’t want to be in the satellite building business. It wants to corner the market on providing processing capabilities to other spacecraft developers.
The first spacecraft on orbit will use sensors and Aethero’s processors to train a computer vision model, which is likely the first time a private company has done that, per Ge. Once the product is proven to work in the space environment, he expects to find initial customers in EO and orbital services industries.
And there are more fanciful ideas: Ge speculated about a future where dozens of orbiting Aethero processors operate in sync, becoming the first space-rated supercomputer.
The next big thing: Chris Bogdan, who leads Booz Allen Hamilton’s space business, told Payload that edge computing in space is among the top tech that’s exciting investors: “If you can put computing at the edge and AI in a satellite, then all the data it collects, it doesn’t have to send down reams and reams of data, it sends down what’s important.”
Ali Partovi, managing director at Neo Ventures, led Aethero’s seed round, which was the first space-related investment from an early-stage investor who has backed firms like Facebook, Airbnb, Dropbox, and Uber
“For us, it’s at the end of the day just a computation investment, closer to software than aerospace,” he told Payload. “This is part of an inflection point, where the other needs of getting things to space have reached a point where it’s more feasible to start building things at the software layer.”
“We’ll look back on today—it was quaint, we used to have to send everything back to Earth and wait for hours,” he says.





