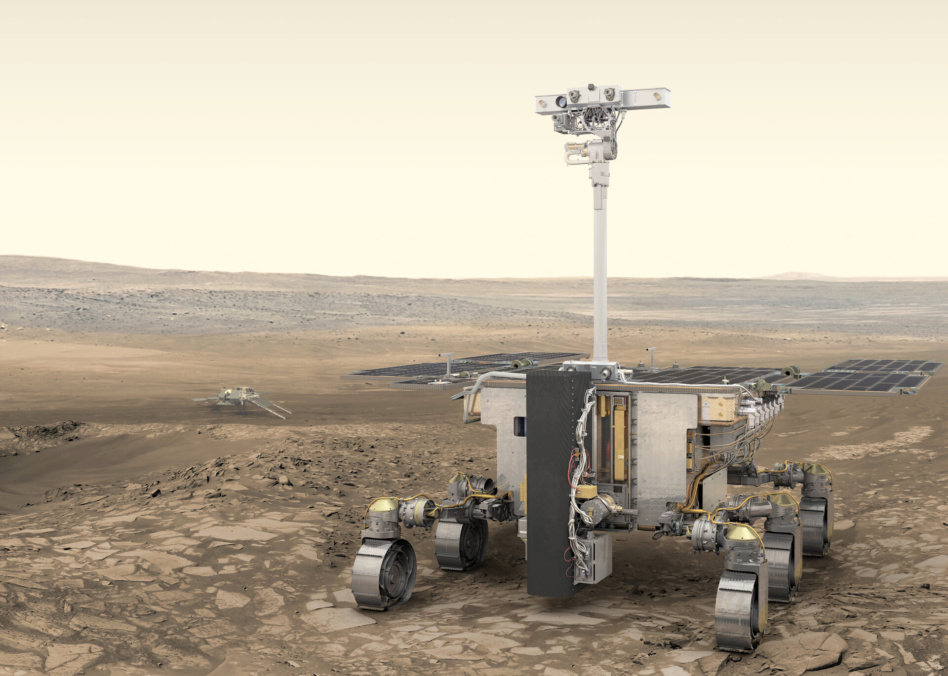
It’s officially official for ExoMars: The ESA’s Mars rover mission will not fly this year.
Yesterday, ESA’s member states voted unanimously to suspend all operations with Roscosmos, the Russian space agency. In response to heavy sanctions, Roscosmos announced Feb. 26 that it would nix future Soyuz launches from French Guiana and pull staff from the spaceport. Now, ExoMars and several other ESA missions that would have flown on Soyuz are left to find another ride to space.
ExoMars: ESA’s Mars rover mission has been in the works since 2001. The mission consists of two components:
- The Trace Gas Orbiter, which has been orbiting Mars and studying its atmosphere since 2016. The orbiter will also act as a communication relay for…
- …Rosalind Franklin, a rover on a mission to find out whether there has ever been life on Mars.
The ExoMars rover was originally meant to launch in 2020, but pandemic complications down on Earth and concerns that the mission’s parachute system wouldn’t be ready in time delayed the launch to Sep. 2022.
Now, it’s being delayed again. Because scientists need to wait for Earth and Mars to be aligned properly in order to launch anything to the Red Planet, there are about 26 months in between launch windows. The earliest possible launch for ExoMars, then, would be in late 2024.
- ESA Director of Human and Robotic Exploration David Parker said at an ESA Council briefing that 2024 is only likely if the agency can mend its relationship with Roscosmos. Otherwise, the agency is looking at a 2026 or 2028 launch.
Other effects: ExoMars isn’t the only ESA mission planned to launch aboard a Soyuz in the near future. A few sets of Galileo navigation satellites, the EarthCare mission with JAXA, and ESA’s Euclid space telescope were all set to launch on Soyuz by 2023. The agency must now find a new ride for these missions.
What now? There’s an extraordinary ESA Council meeting planned for mid-April, where the member states will discuss alternative launch solutions and European reliance on Russian components.