It seems like every agency in Washington is taking a closer look at satellite constellations these days. That extra attention may lead to new hoops for satellite operators to jump through.
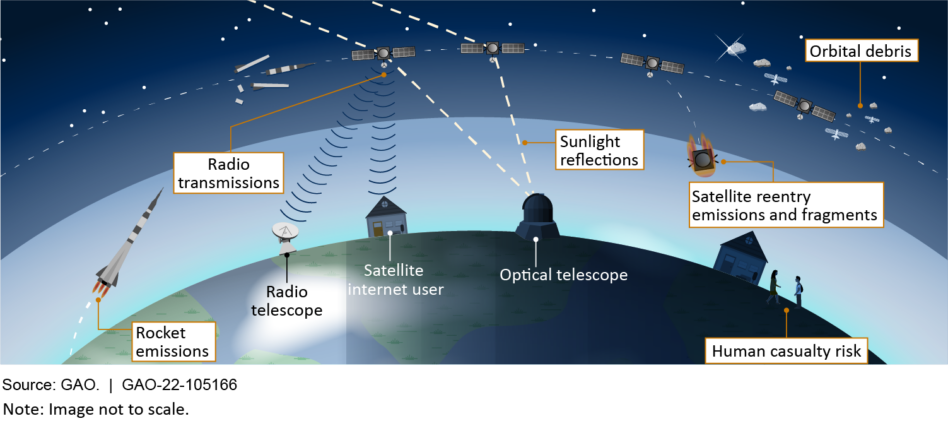
Last week, the US Government Accountability Office (GAO) released a report on megaconstellations. GAO noted that new, growing fleets of satellites drive direct value back to Earth, from geolocation to connectivity services. But they also have negative externalities. GAO highlighted three:
- A build-up of orbital debris
- Upper atmospheric emissions
- Disruption to astronomy
The findings
GAO concluded that scientific understanding of launch emissions and their effect on the atmosphere is minimal, largely due to the lack of observational data. It’s time-consuming and expensive to track this information.
The office also established that satellite re-entry fragments may pose risks to humans, but that private and public players are actively working to mitigate these dangers.
Lastly, the report looked at the effect on space systems and astronomy, finding that effects on sunlight reflection and radio transmission may be challenging to fully eliminate. The findings also noted potential cultural implications. Sunlight reflected from satellites could alter our view of the night sky and affect some Indigenous groups’ interactions with it, GAO wrote.
“In a few short years, large proliferated systems, with anywhere from dozens to thousands of satellites, have gone from theory to cementing themselves as part of our shared space future,” Luc Riesbeck, space policy research analyst at Astroscale US, told Payload. “For all the benefits they will bring, we need to take stock of the real-world impacts of fielding space systems and launch cadences of these magnitudes.”
GAO provided options for policymakers, rather than handing down recommendations. Those policy options are split into four buckets:
- R&D—policymakers could support research into new technologies. Darkened satellites and active debris removal are two examples provided.
- Sharing is caring—Governments could incentivize (or compel) constellation operators to share data more freely and efficiently.
- Standards, rules, & regs—Licensing could become more standardized.
- Create org charts—At the national and/or global levels, policymakers could vest more control into a body that mitigates the potential effects of megaconstellations.
“The big takeaway from this report is that there’s still much more work to be done to proactively sustain our collective use of space for the long term,” said Riesbeck.